The Modern Retailer’s Guide to Omnichannel Fulfillment
Omnichannel fulfillment enables retailers to deliver seamless shopping experiences by connecting online, in-store, and third-party channels under a unified fulfillment system.
Modern customer expectations demand fast, flexible fulfillment options like BOPIS, ship-from-store, and real-time inventory visibility across all locations.
A well-executed omnichannel strategy leads to faster delivery, reduced costs, improved inventory turnover, and greater customer retention, positioning retailers for long-term growth.
fabric OMS offers enterprise-level features and functionality to effectively manage orders, inventory, and fulfillment across multiple channels, enabling retailers to deliver a seamless customer experience.
updated on July 14, 2025
We live in a modern retail world where seamless delivery is necessary. Modern commerce demands an omnichannel fufillment approach that goes far beyond traditional channel silos, ensuring every order is connected across multiple sales channels and delivered quickly and reliably.
Customers these days expect a frictionless experience regardless of when and where they shop—online, in-store, or through marketplaces. Recent data from the U.S. Census Bureau shows that e-commerce sales reached $300.2 billion in the first quarter of 2025, making up roughly 16.2% of total retail sales. This shift highlights the importance of adapting your fulfillment methods to meet the increasing expectations of customers and the growing number of sales channels.
While many retailers are moving towards omnichannel fulfillment services, achieving efficiency at scale across multiple selling channels and diverse physical stores is still a significant challenge. Without a robust approach, fragmented and in-house fulfillment operations can lead to delays, errors, higher costs, and ultimately, lost sales and declining customer satisfaction.
In this article, we’ll review what omnichannel fulfillment means, why it matters for enterprise retailers, and how to do it right.
What is omnichannel fulfillment?
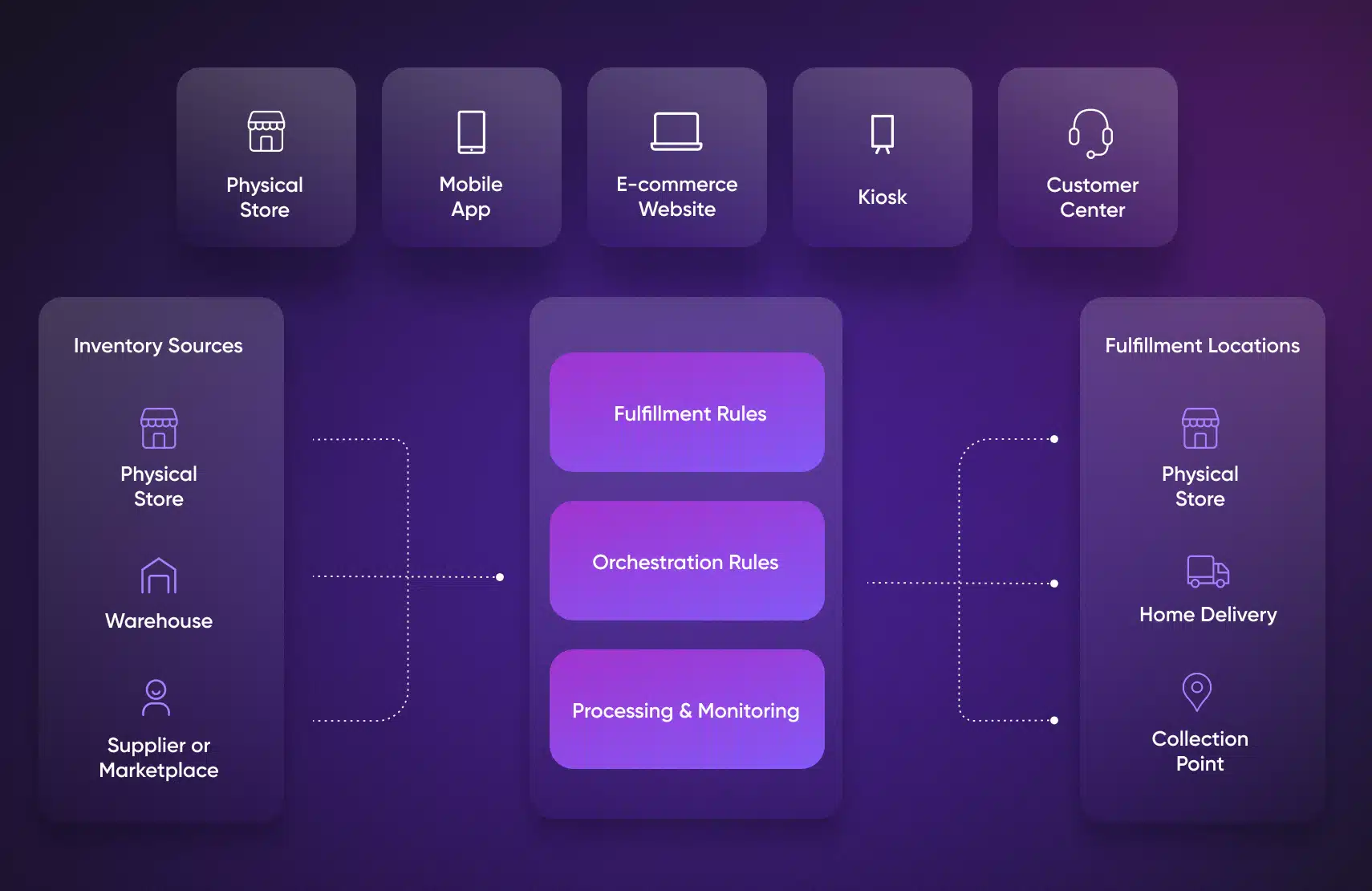
Omnichannel fulfillment is the ability to fulfill customer orders across any channel—online, in-store, or third-party—using a connected inventory and logistics network.
In practice, this means you can efficiently fulfill customer orders regardless of where they originate, making it seamless for your customers to shop, pick up, or return across multiple sales channels.
Here are some common examples of fulfillment methods that enable this:
- BOPIS (Buy online, pick up in-store)
- BORIS (Buy online, return in-store)
- Ship-from-store leveraging physical stores as micro-fulfillment hubs
- Fulfillment from third-party marketplaces like Amazon or Walmart Marketplace
- Local delivery or same-day options for improved customer satisfaction and timely delivery
Modern retailers are increasingly adopting these approaches to meet rising consumer expectations and remain competitive across various channels. 45% of shoppers expect same-day pickup from the physical stores, highlighting how vital flexible fulfillment has become for customer satisfaction and a consistent online shopping experience.
By connecting your existing physical infrastructure, online stores, and other offline sales channels within a single, seamless order fulfillment ecosystem, you can deliver a seamless shopping experience for every end customer.
Why omnichannel fulfillment matters
Modern retail has evolved far beyond basic online ordering. These days, customers expect a seamless, fast, and flexible delivery, making omnichannel fulfillment a critical element for retail success.
Some of the significant factors, as to why it matters, are:
- Rising customer expectations: Shoppers expect the ability to shop, pick up, and return across multiple sales channels—online, mobile, or in-store.
- Intense competition from marketplaces: Amazon and other major marketplaces have set a high standard for timely delivery and customer experience, compelling retailers to adapt their fulfillment strategies to stay competitive.
- Growing pressure to reduce fulfillment costs: Amid rising supply chain and labor expenses, you must optimize how to efficiently fulfill orders across different sales channels to protect your margins and maximize your ROI.
- Live inventory update: Real-time inventory information provides a consolidated view of your inventory across multiple selling channels. An integrated inventory tracking system can help you ensure timely delivery and exceed consumer expectations.
- Margin pressure and the need for efficiency: Managing inventory counts, order fulfillment, and returns across diverse locations and various sales channels is complex. You must optimize every link in your supply chain to reduce operational waste and protect profits.
Challenges retailers face without modern omnichannel fulfillment
If you’re relying on traditional, fragmented fulfillment methods, you’ll often struggle with long-term systemic pain points that hinder growth and impact customer satisfaction:
- Manual fulfillment workflows often lead to delays and error-prone deliveries, which can frustrate customers.
- Separate inventory management across online stores, brick and mortar, and warehouses results in overselling popular items or missed sales opportunities.
- Overwhelmed store teams, who handle BOPIS, in-store purchases, and returns, struggle to balance daily retail priorities.
- Split shipments drive up shipping costs and diminish margins as your team manually tries to piece orders together from disconnected inventory pools.
- A lack of data and visibility across multiple sales channels makes it challenging to optimize order fulfillment decisions, resulting in higher operational costs and decreased customer loyalty.
Core capabilities of a strong omnichannel fulfillment strategy
To meet rising customer expectations across multiple sales channels, you must adopt a set of core capabilities that enable seamless order fulfillment across all sales channels.
Here’s a checklist of advanced capabilities you need:
Real-time inventory visibility
Accurate inventory visibility is the foundation for a successful omnichannel fulfillment strategy. You can efficiently fulfill orders and prevent overselling or stockouts by providing a consolidated view of available stock across your physical stores, distribution centers, and third-party locations.
Research shows that 43% of small businesses don’t track inventory, making it challenging to maintain and track accurate inventory counts across multiple sales channels. An integrated inventory tracking system can remove this barrier and help you ensure precision across every channel.
Automated fulfillment decision-making
You need to adopt intelligent, rules-based routing that automates the decision on how to fulfill customer orders most effectively. By leveraging data like store location, available inventory counts, delivery speeds, and costs, you can reduce delays, optimize fulfillment methods, and lower operational expenses across multiple sales channels.
Store-level enablement
You can transform brick-and-mortar stores into dynamic micro-fulfillment centers by supporting services like buy online, pick up in-store (BOPIS) and ship-from-store. This approach enhances timely delivery, expands the range of available fulfillment methods, and provides a seamless experience across both online and offline sales channels.
Unified order and returns management
Your customers will expect a consistent experience across all your channels, including a seamless returns process. A strong omnichannel fulfillment model provides a single view of all orders, making returns and exchanges smooth and convenient regardless of channel. This enhances customer loyalty and fosters trust throughout every shopping experience.
Flexible carrier and delivery integrations
You must work with a network of carriers and delivery services across national and regional providers. A robust order fulfillment solution supports a seamless shipping system, enabling you to adapt to fluctuations in demand, geography, and costs. This makes offering options like home delivery, in-store pickup, and local delivery more straightforward.
Scalable infrastructure
Operating across complex ecosystems requires connecting ERP, OMS, WMS, and 3PL platforms for end-to-end visibility and operational efficiency. A robust, scalable infrastructure built for growth can empower you to launch new sales channels, adapt to market shifts, and optimize across global supply chains.
Benefits of omnichannel fulfillment done right
By implementing omnichannel order management and fulfillment strategies, you can unlock a range of benefits across your sales channels, yielding higher revenue, improved customer satisfaction, and more resilient fulfillment operations:
- Faster delivery = higher conversions: Leveraging multiple selling channels can reduce order fulfillment times, making shoppers more likely to complete their online purchases.
- Reduced fulfillment costs through smart sourcing: Intelligent order fulfillment rules and integration of online stores enable you to locate the most cost-efficient source for each order, significantly reducing shipping and operational expenses.
- Higher inventory turnover and reduced overstocks: Gaining inventory visibility across all sales channels allows you to balance inventory more effectively, reduce excess stock, and keep inventory counts aligned with actual consumer expectations and sales trends, minimizing markdowns and increasing turnover.
- Improved customer satisfaction and retention: An effective omnichannel strategy ensures seamless order fulfillment, making it easy for your customers to shop across different channels and have their purchases delivered quickly or picked up in-store. This customer-centric approach improves customer loyalty and long-term satisfaction.
- Flexibility to adapt: A robust fulfillment company infrastructure allows you to launch new sales channels quickly, adopt an online marketplace, or expand your offline sales channels. The ability to scale can give you a competitive edge in responding to evolving consumer expectations and market trends.
How to build a modern omnichannel fulfillment strategy
Considering the evolving market trends and customer preferences, you must rethink how you connect all your sales channels to deliver seamless order fulfillment and a superior customer experience.
Here’s how you can build a forward-looking multi-channel fulfillment strategy that can deliver across multiple sales channels and scales for the future:
Centralized inventory visibility
Break down silos by creating a single view of inventory counts across all your sales channels and locations. An integrated inventory tracking system allows you to unify data across online stores, physical stores, and fulfillment centers, making it possible to fulfill orders efficiently.
Unify order data and standardize fulfillment logic
Standardize rules for order fulfillment across different channels to reduce split shipments, delays, and errors. Centralizing order and customer data can build a seamless experience that improves customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Enable store-level fulfillment
Train all your teams to operate as micro-fulfillment hubs. By supporting BOPIS and ship-from-store capabilities, you can optimize existing physical stores and expand fulfillment methods to suit the needs of your end customers.
Automate fulfillment routing
Deploy intelligent routing to direct orders to the best fulfillment centers, stores, or third-party locations based on proximity, cost, and available inventory counts. This improves efficiency across multiple channels and ensures timely customer delivery.
Integrate existing systems
Connect every link of your retail supply chain—OMS, WMS, POS, ERP, and third-party logistics providers—for end-to-end visibility across all fulfillment methods. A seamless technology stack allows you to scale quickly, launch new online marketplaces, and adapt to rising consumer expectations.
Measure performance
Continuously track key metrics, such as order processing timers, cost per order, inventory count accuracy, and customer satisfaction. Performance measurement is crucial for identifying bottlenecks and fine-tuning fulfillment strategies across your sales channels.
Continuous optimization
Use analytics to adjust your omnichannel order fulfillment approach in real-time, aligning fulfillment methods with customer preferences. By leveraging data-driven insights, you can balance inventory across all sales channels, reduce split shipments, and adapt quickly to market trends.
The future of omnichannel fulfillment
The future of retail is being shaped by how well businesses can connect every order, every channel, and every piece of inventory into a seamless, unified experience.
Consumer expectations have evolved beyond traditional boundaries, and to win in the competitive market, you must unite your sales channels under a common fulfillment strategy.
With the proper infrastructure, you can do more than satisfy rising customer expectations. You can exceed customer expectations, reduce operational waste across your supply chain, and position your business for long-term resilience and growth.
If you’re ready to explore how this approach can work for your business, we’re here to help. Contact us to discuss your omnichannel requirements and challenges, or request a demo to see how fabric can enable seamless order fulfillment and drive long-term retail growth.

Digital content editorial team @ fabric