What Is Magento 2 Order Management and Its OMS Alternatives?

Magento started in 2008 as an open source e-commerce platform. While its open source platform is popular among smaller e-commerce retailers, the premium version has an expanded feature set that becomes necessary to grow.
Magento’s most recent update, Magento 2 order management system (OMS), fixed some issues that boosted the platform’s performance in 2015. Support for Magento 1 ended in 2020, and since then, Magento has grown to support around 12% of online retail stores. While the update has improved the OMS, Magento 2 has pros and cons to weigh against other competing platforms.
[toc-embed headline=”Magento 2 Order Management Features”]
Magento 2 Order Management Features
Advantages of Magento 2 order management
Magento 2 has features that attract e-commerce stores. One of the most significant is its efficient checkout design. A one-page checkout process can perform 20% better than a multi-step checkout. Magento makes it simple to set up a one-page checkout, distinguishing it from other e-commerce platforms.
This checkout functionality integrates with OMS Magento to create a seamless transfer of information between the systems. The result is fewer mistakes and human error. Thus, Magento’s order management is useful for B2B companies covering everything from quote creation to order fulfillment.
Magento’s other advantages include secure payment methods, a powerful search engine, and managing multiple channels simultaneously. This is useful for both B2C and B2B e-commerce. In addition, Magento touts its flexibility as a key differentiator against other competitors like Shopify. Magento’s user interface is also a plus due to its intuitive layout.
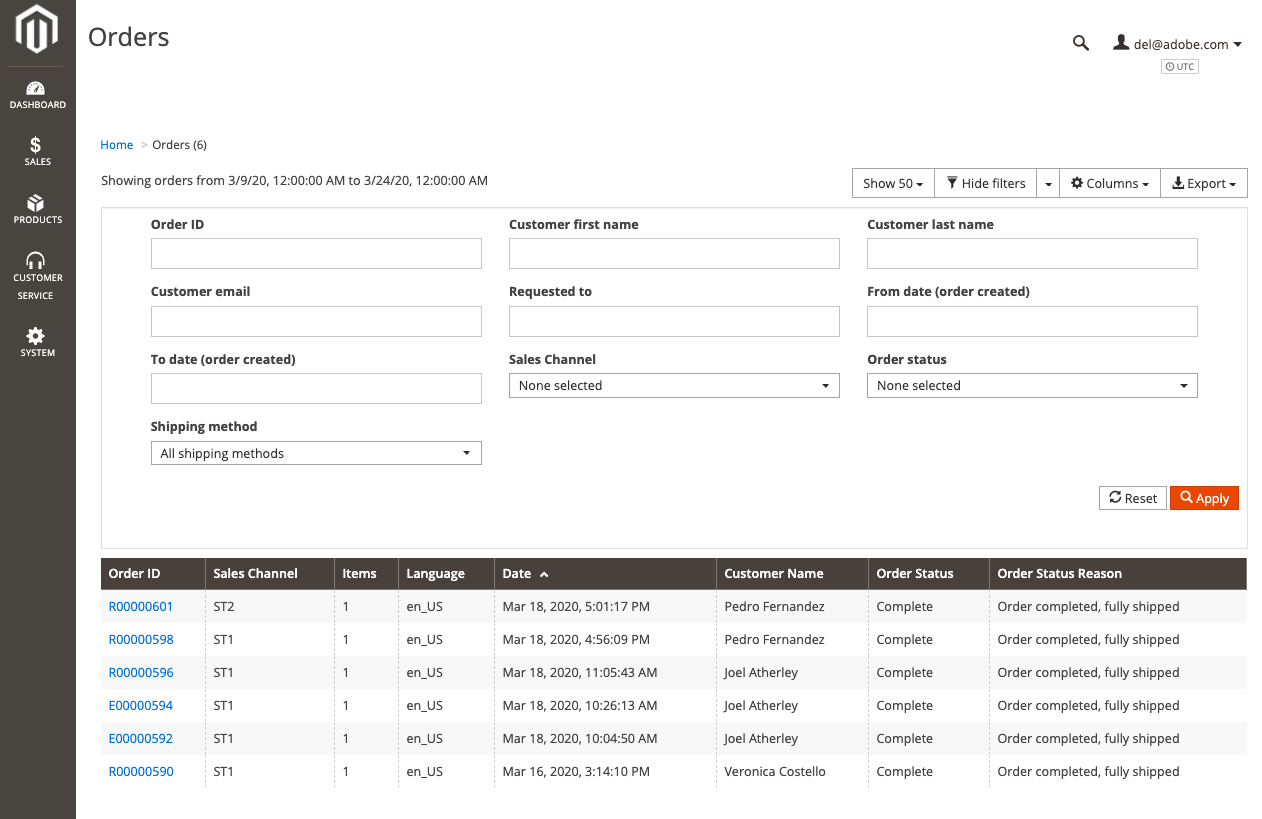
Disadvantages of Magento 2 order management
A complete evaluation of Magento OMS shows its monolithic architecture hampers its features. As an e-commerce solution and an OMS, Magento 2 has many of the features for which its customers are looking. But it doesn’t let users pay for and use individual functions like the OMS. Instead, they must pay for the single, monolithic platform.
Many enterprises find themselves with significant technical debt after using the same monolithic platform over time. Different components of the platform may be updated at different times, depending on the company’s decision. This leaves users with out-of-date technology to use.
To pay off the technical debt, users need to deconstruct the monolithic platform, a process that can be time-consuming and expensive. The alternative is relying on legacy systems that incur an “e-commerce tax” from the expense of maintaining them.
[toc-embed headline=”Alternatives to Magento 2 Order Management”]
Alternatives to Magento 2 Order Management
It’s essential to compare Magento 2 against both legacy and modern alternatives. The traditional platforms have monolithic architecture like Magento and had more time to develop deep feature sets. On the other hand, modern headless commerce platforms can have even greater flexibility.
Traditional OMS alternatives
- Oracle has been developing its OMS since 1993, which has let it create a deep set of features still used by many enterprises today. However, its long history is also why it has a legacy architecture that holds it back from the flexibility modern businesses demand.
- SAP Hybris is a similar platform with a long legacy. Like Oracle, it’s a monolithic, Java-based order management system popular with larger enterprises. However, many users incur technical debt with Hybris.
- Demandware or Salesforce Commerce Cloud has the unique advantage of vetted integrations that Magento users cannot access. However, it’s challenging to use and the most valuable integrations cost extra, even for users already paying enterprise prices.
Modern OMS alternatives
- Shopify’s headless commerce system puts it in the more modern category of OMS platforms. But the e-commerce giant has plateaued due to its rejection of cutting-edge microservices architecture in recent years.
- BigCommerce also has a headless architecture that lets users customize the platform to their needs. But it still forces users to adapt their use to the company’s decisions rather than build the system they need for themselves.
- fabric microservices to let users pick what features they need from an OMS. The result is a secure and flexible platform wrapped in an intuitive user interface that compares well against other OMS options.
[toc-embed headline=”Key Takeaways”]
 Key Takeaways
Key Takeaways
- Despite its intuitive interface, Magento 2 order management has a monolithic architecture that prevents customization.
- Legacy OMS alternatives also lack flexibility and don’t all have the features available on more modern platforms.
- Even some modern alternatives like Shopify and BigCommerce use headless architecture but lack the microservices that leading companies use to personalize their OMS to their use-cases.
- fabric OMS uses a microservices architecture to deliver the features customers need without paying for unnecessary services.

Tech advocate and writer @ fabric.
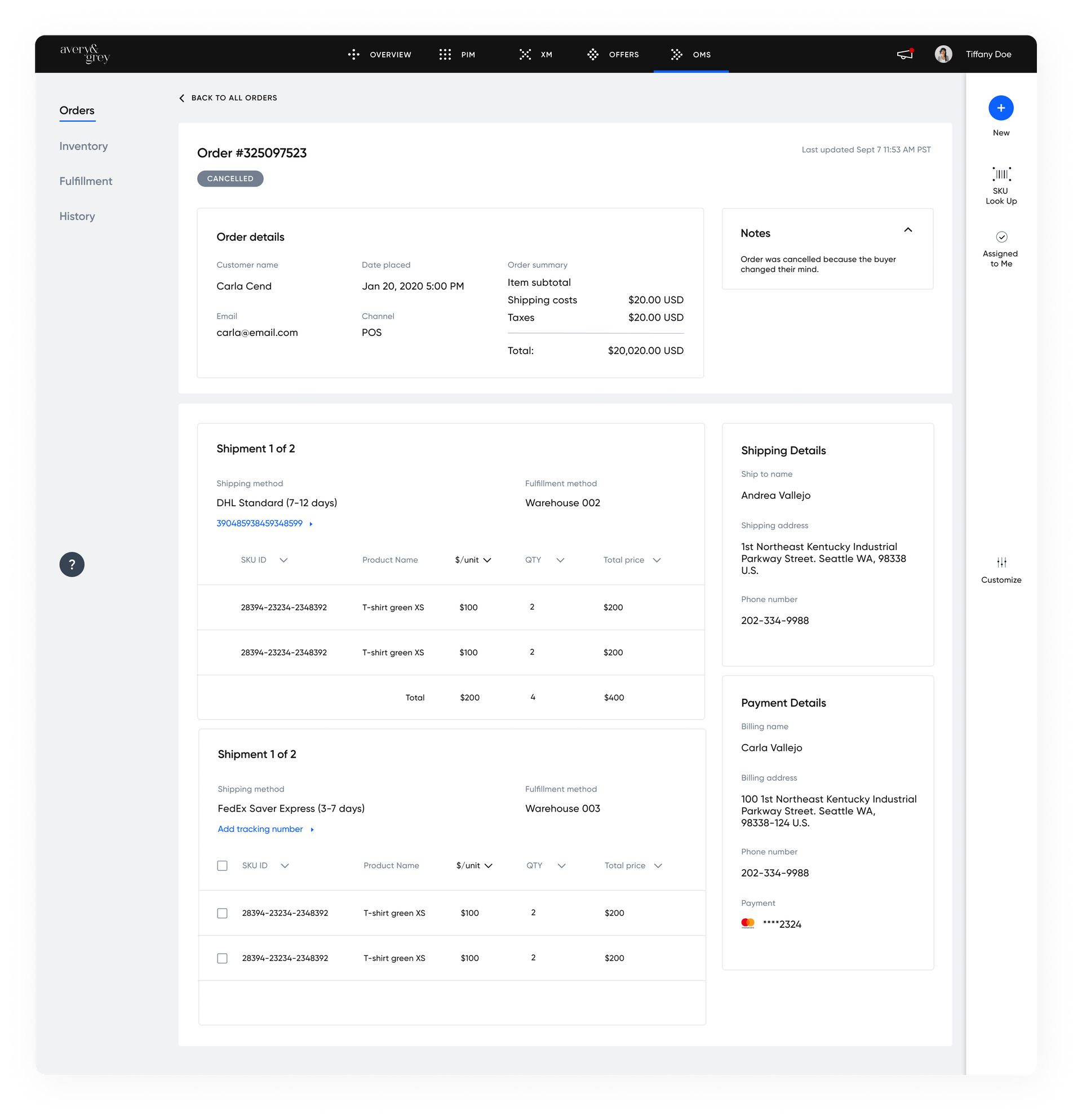 Key Takeaways
Key Takeaways