What Are the Benefits of Order Management Database Structure?
Are you one of the 69% of businesses still using spreadsheets in place of automated order management systems? While spreadsheets help with data organization, they increase the risks of order fulfillment issues, such as late shipping, understocking, and overstocking.
As you expand your business into multiple marketplaces, it becomes harder to track and unify all your customer data. A good order management database structure prevents these issues by simplifying customer data collection and increasing data accuracy.
In this article, we’ll discuss the importance of building a good order management database structure and how to start building one.
[toc-embed headline=”Advantages of Order Management Database Structure”]
Advantages of Order Management Database Structure
An order management database structure refers to the grouped data within an order management system (OMS) software. This software separates these grouped data, like customer names and IDs, orders and order details, and products and availability, into tables and rows for clarity and accuracy when managing, processing, and fulfilling customer orders.
Order management structures help businesses process order-to-cash transactions made by customers after interaction with your sales channels. These channels include online stores, mobile shopping apps, and in-store point-of-sale (POS) systems.
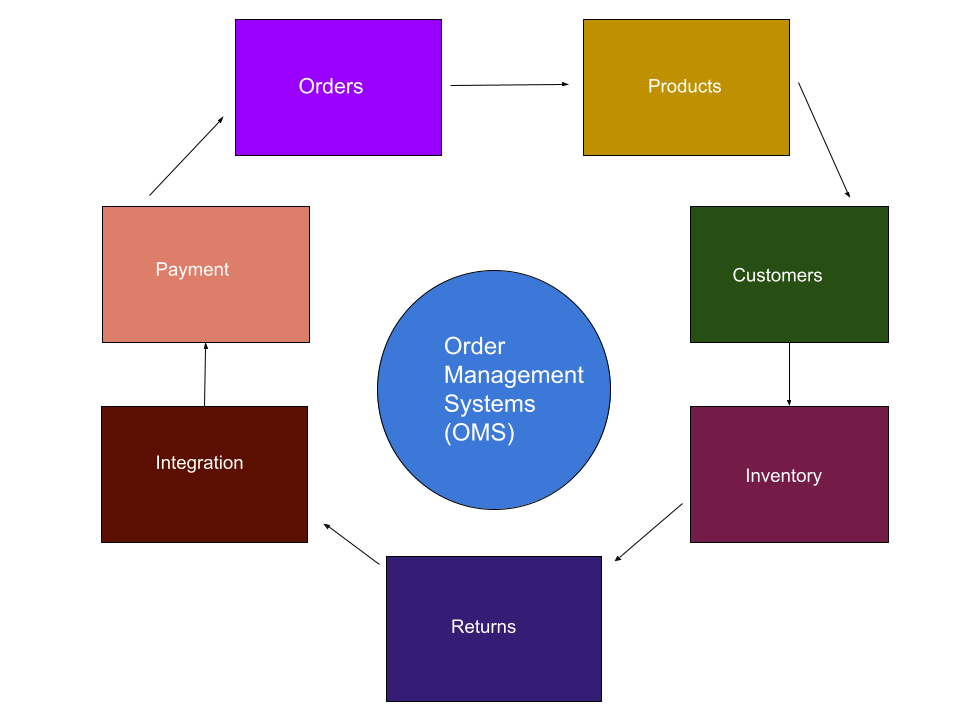
The advantages of a fully functional order management database structure include the following:
- Data organization and disk space decluttering: A good database structure reduces data error and redundancy, which are associated with manual labor in data entry. For example, you can use primary and foreign keys to link related customer data. That way, you eliminate duplicate data that can mislead business decisions.
- Key performance indicators (KPIs) analysis: Order database structures help businesses analyze KPIs. These are sales patterns that are used to measure the overall performance of the business. This way, companies make more informed decisions and are able to predict their future performances.
- Inventory management: An order management database structure ensures uniformity across all your marketplaces. This ensures your sales channels reflect the right amount of products available in stock. With real-time customer order data, you can avoid costs incurred from overstocking or losing customers from running out-of-stock.
[toc-embed headline=”Building an Order Management Database Structure”]
Building an Order Management Database Structure
Decide on what OMS to use
The ideal OMS should reflect your inventory in real-time and reduce data processing errors. It should also process customer orders quickly as 62% of customers define fast shipping with great customer experiences. Customers want to know that the moment they hit the order now button, you’re already processing their order.
Choose a database type and infrastructure
Depending on your requirements, your database infrastructure can either be managed or unmanaged. Managed database infrastructures are controlled by third-party providers instead of business teams. Unmanaged infrastructures allow business teams to have administrative access and full control of the software.
Database types range from NoSQL databases to relational or key-value databases. Businesses with unstructured data may want to consider the NoSQL databases like MongoDB. On the other hand, businesses with structured data typically use relational databases like the Microsoft SQL Server.
Collect customer data
Using OMS to collect customer information will help you tailor a personalized experience for your customers. You can recommend products or services that customers are most likely to purchase in their next order. You can also predict your sales from the data you retrieve from sales channels. This will help recognize customers with high-profit potential.
Group customer data
The next phase of building an order management structure involves categorizing your data into tables. This process gives business owners clarity when analyzing the data. For example, on your order management structure, you can arrange customer names, addresses, products, and quantities under separate columns.
Create and assign primary keys
You can assign primary keys to categorize customer data in your structure. The primary key is a unique identifier, such as 1 or 001. You can use it to find a particular customer’s information within the OMS software. The primary key can also be a number specific to a product. This lets you find information from any table whenever you need it faster.
Establish unique table relationships
At this stage of your order management database design, you can match similar rows and columns of customer data with your primary keys. For example, when one customer orders multiple items, you can use the primary key to indicate a relationship between their personal information and their order. When that happens, the primary key becomes a foreign key.
So whenever you need to change a primary key, it’s crucial that you alter its entry in other rows and columns where it is referenced.
[toc-embed headline=”Key Takeaways”]
Key Takeaways
- 68% of businesses still use spreadsheets in data collection, which increases the risks of order fulfillment issues.
- Order management structures prevent order fulfillment issues by automating customer data collection to increase data accuracy.
- Collecting and grouping data within an order management structure helps businesses predict sales and long-term performances.
- fabric OMS offers an intuitive solution for fast and easy management of customer orders and business inventories.

Tech advocate and writer @ fabric.