Order Routing: The simplest and fastest way to optimize fulfillment—without writing code
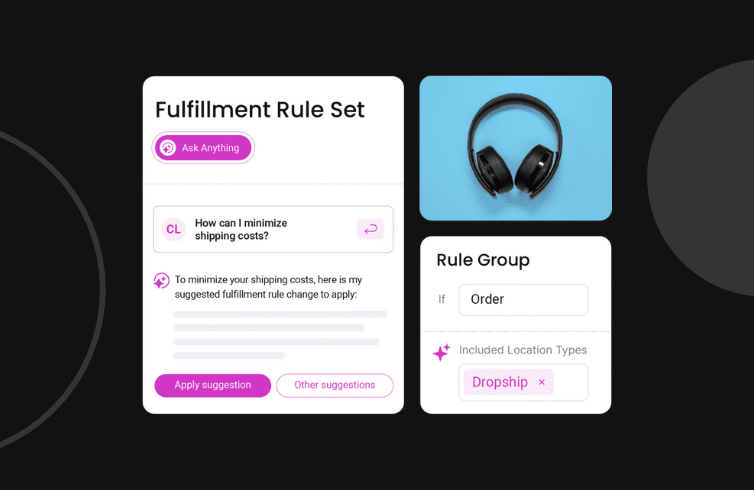
With fabric OMS, any retail operator can configure order routing rules to reduce order errors, get closer to customers, and reduce shipping expenses.
As businesses grow, so does the complexity of allocating resources to fulfill customer orders across multiple locations. While introducing more fulfillment centers can increase your capacity and get you closer to customers, it can also become a logistical challenge that can negatively impact operations.
For example, today’s retailers need to:
- Get real-time inventory snapshots of what stock they have across their network at any given time.
- Prioritize orders by urgency, customer importance, or other business rules.
- Determine which are the best locations to ship orders from.
- Coordinate with other systems to ensure a seamless flow of information and execution.
- Calculate the distance, time, and cost to deliver orders, all in an instant.
When confronted with a myriad of orders flooding your store, it becomes increasingly more difficult to manage inventory, order, and fulfillment processes across multiple sales channels and fulfillment locations.
To get products to shoppers fast, enterprise retailers require a decision engine that can seamlessly allocate inventory and fulfill customer orders. A powerful order management system (OMS) that features order fulfillment logic (OFL) can seamlessly route orders to the best locations to fulfill orders from.
What is OFL?
OFL refers to logic-based rules that make decisions about where a company routes its orders for optimized fulfillment. In fabric OMS, this order fulfillment feature allows a business to create fulfillment rule sets that direct orders to different fulfillment locations based on characteristics, such as geo-location, warehouse location, item price, order attribute type, and more.
[toc-embed headline=”Development vs. no-code configuration for OFL”]
Development vs. no-code configuration for OFL
In commerce, the choice between configuration and development for OFL often depends on an organization’s resources, money, time, and expertise. In theory, development is a great option because it provides unlimited customization and complete control over the solutions you build. However, without a proficient combination of retail and technology expertise, costs can run amok while delays pile up. It also becomes very easy to develop redundant and often unnecessary functions that don’t actually address pain points or improve the customer experience.
On the other hand, configuration is only as good as the use cases they address. For example, Shopify’s smart order routing service only supports 4 main rules out of the box. Retailers are severly limited to what they can and can’t configure with their order routing engine.
Today, it is not enough to simply grant non-technical users the ability to configure OFL without writing code. Enterprise businesses need to get products into the hands of customers quickly and cost-effectively. They also require flexibility to tackle different fulfillment scenarios—some of which they’ve never encountered before. A highly-configurable solution that supports a variety of different use cases can help lower costs and deliver on speed, efficiency, accessibility, and adaptability.
[toc-embed headline=”fabric OMS supports more OFL use cases than other solutions”]
fabric OMS supports more OFL use cases than other solutions
fabric OMS allows more configuration of order routing rules and supports more use cases through OFL than other fulfillment solutions in the market. This includes Salesforce, Shopify, and other platforms with self-service UIs.
Once an order is created, fabric’s allocation module and OFL will automatically route the order to the optimal location based on the parameters and rules set by the retailer. As a high-performance OMS, some of the OFL use cases include:
Routing orders to optimal locations for omnichannel fulfillment
Routing orders to the best locations for buy online, pickup in store (BOPIS), curbside pickup, or ship from store enhances customer convenience by directing orders based on the chosen delivery method. With features around location management such as capacity and outage planning, this use case accelerates and streamlines order fulfillment, optimizes inventory levels across locations, reduces operational complexities, and improves the overall shopping experience.
Setting up geographic bands to select the location nearest to the customer
To improve speed and efficiency, retailers need to ensure that products are sourced from the closest inventory point. By fulfilling orders based on availability and from locations within a set radius of the customer, retailers can minimize shipping distances, reduces delivery times, prevent fulfillment bottlenecks, and improve customer satisfaction through fast and localized delivery.
With fabric OMS, retailers can take this one step further. Within a given geographic band, they can set rules to pick from which location is best, based on capacity, inventory, and available services. This is a key differentiator for fabric OMS in terms of its capabilities.
Configuring automatic reallocation for no-inventory situations
Retailers also need to be proactive when managing customer expectations. To prevent potential disappointments, this use case ensures that orders are automatically reallocated when inventory shortages occur, allowing businesses to fulfill on time, maintain transparency with customers, and focus on fulfilling orders with available stock.
Configuring split shipment rules
fabric OMS offers flexibility and customization when it comes to configuring split shipment rules. Unlike other platforms with static split shipment rules, fabric allows for a stack of parameters, enabling retailers to define their preferences more precisely.
For instance, retailers can set conditions to initially prioritize fulfilling orders without split shipments first before resorting to conditions that accept split shipments if necessary. Configuring split shipment rules enables retailers to efficiently handle complex orders with greater control and adaptability.
Using order and product metadata to set rules
Retailers can also tailor their fulfillment processes based on specific characteristics found in order and product attributes. Users also have the ability to set fulfillment location types (such as store or distribution center), name rules, and set descriptions. These configurable rules provide businesses with far greater control, and ensures a more targeted and responsive strategy to order processing.
Instead of generically applying rules to all of your orders, you can apply the right rules to the right orders. For example, if orders contain Army Post Office (APO) or Fleet Post Office (FPO) shipment data, fabric OMS can ensure they’re routed to the right fulfillment facility for that use case.
[toc-embed headline=”The industry’s first commerce platform with native OMS to optimize the post-purchase experience”]
The industry’s first commerce platform with native OMS to optimize the post-purchase experience
With fabric OMS, today’s omnichannel retailers gain advanced no-code order routing capabilities to simplify the order fulfillment process across multiple channels. Non-technical retail operators can easily configure OFL to route orders to optimal locations, which can lower costs and maximize speed and efficiency.
For any business looking to optimize their processes, the benefits are clear: with a streamlined and highly customizable approach to order management, retailers can get products to customers faster, thereby improving operations, enhancing customer satisfaction, and ultimately driving more profitable operations.
If you’re interested in learning more about fabric OMS and see how our no-code OFL rules engine works, feel free to schedule a demo with us.

Digital content editorial team @ fabric