What is an API Call? A Developer’s Introduction to API Calls for E-Commerce
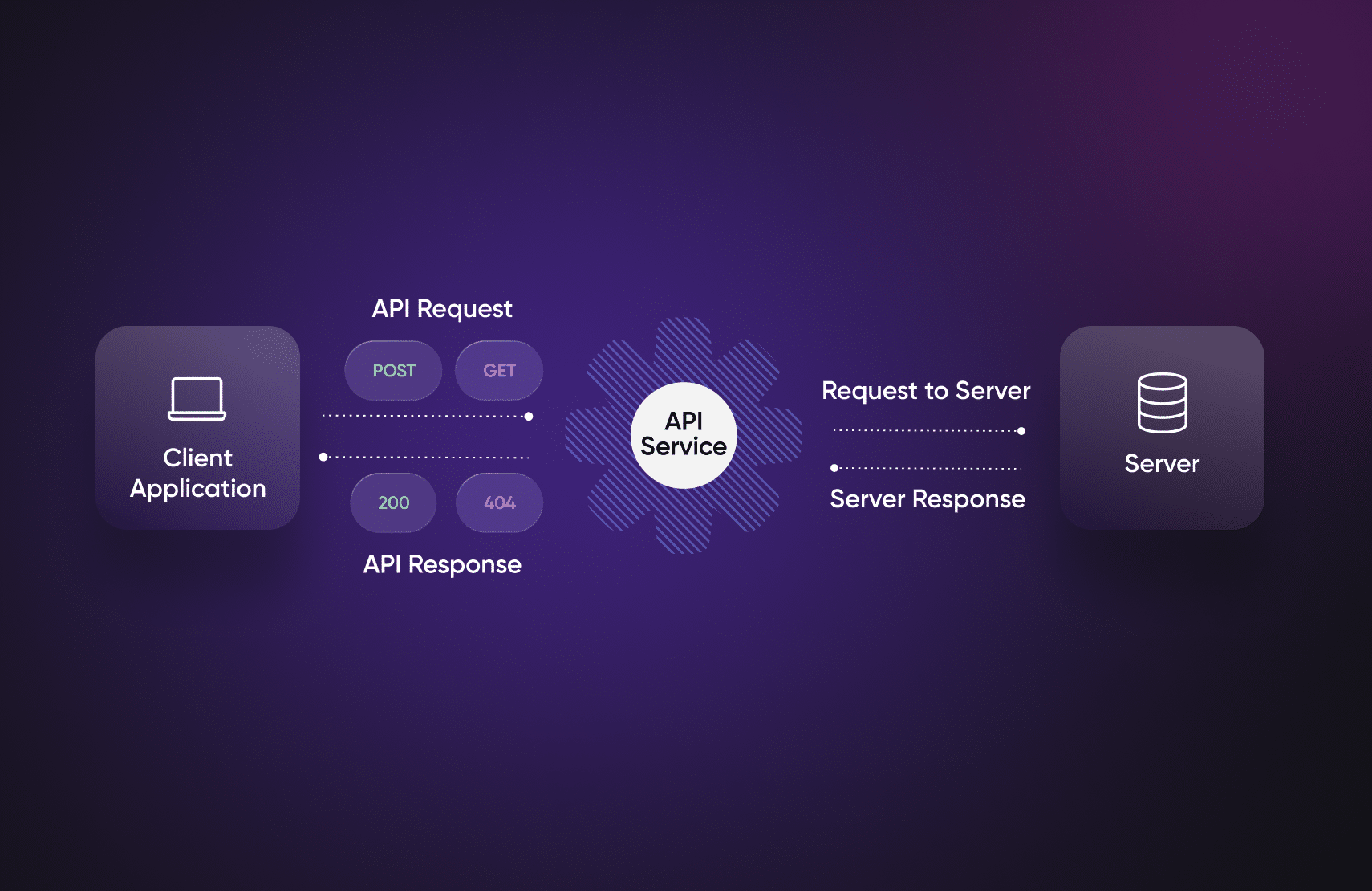
An API (application programming interface) call is a request made by a client to a server to access or exchange data based on rules defined by an API.
E-commerce API calls come in various types—GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE—each playing a vital role in enabling tasks such as retrieving product data or processing orders.
Efficient and well-executed API calls can ensure efficient communication and swift data transactions, streamlining e-commerce operations and improving the user experience.
API calls optimize operations and enhance functionality within the fabric Commerce Platform, which offers APIs for cart & checkout, inventory, order management, payment integrations, marketplace, and more.
Venture capitalist Marc Andreessen famously once said that software is eating the world. But dig a little deeper, and you’ll find that APIs are what allow modern systems to talk to each other, exchange data, and share services. Therefore, increasingly sophisticated APIs are actually the driving force behind the rapid rise of data-driven applications.
However, you can’t have APIs without API calls. API calls are the lifeline of modern e-commerce, serving as the invisible threads that connect digital platforms and enable seamless interactions. While an API allows applications to communicate with each other, an API call is a way for a client to interact with the server and exchange the data.
APIs and API calls
API calls are usually made to get, modify or send information. Businesses can use existing functionality through API calls – saving developers time with faster implementation. Using API calls, there is no need to reinvent the wheel in e-commerce.
APIs provide a quicker approach to meet rising customer expectations. Businesses can focus on providing the best customer experience by making different API calls to manage and automate their e-commerce operations and transactions. Overall, proper use of API calls can help achieve several benefits like customization, improved shopping experiences, better security, and omnichannel experiences.
[toc-embed headline=”What is an API Call? API Calls for E-Commerce Explained”]
What is an API Call? API Calls for E-Commerce Explained
An API call is a way for client applications to request data from external servers using APIs. They’re used to access specific functionalities or data, following predefined rules and protocols for communication.
Let’s take an example of an online shopping cart. When a shopper checks out, there are multiple API calls made in the background to different applications.
One API call is made to the payment system to verify the payment details. Another call is made to get inventory details of items in the cart. Additional calls are made to verify shipping information, place the order, and so on. Data is exchanged or updated in multiple systems, making the entire checkout operation seamless to the shopper.
The simple step of checking out a cart involves lots of moving pieces in the background. Hence usage of APIs in the current world of ecommerce is significant and can help deliver a seamless shopping journey.
API calls are made in everyday e-commerce operations at various levels:
- 1. Inventory Management API call – To help organize and manage products within inventory
- 2. Payments API call – To provide flexibility and security for shopper to use different payment options
- 3. Pricing and Promotions API call – To provide different pricing and promotions depending on customer segment, channel, etc…
- 4. Order Management API call – To place and track orders for customers.
Performing different API calls for simple and modular actions can enable businesses to create an e-commerce ecosystem based on their customer needs. Businesses can achieve unique shopping experiences with the front end of their choice and different API calls using headless commerce.
[toc-embed headline=”The Anatomy of API Calls”]
The Anatomy of API Calls
API calls are performed based on certain guidelines which define how and what data can be shared, with REST, SOAP, and RPC being popular architectural styles. This section will be focusing on REST APIs and explore their structure and components.
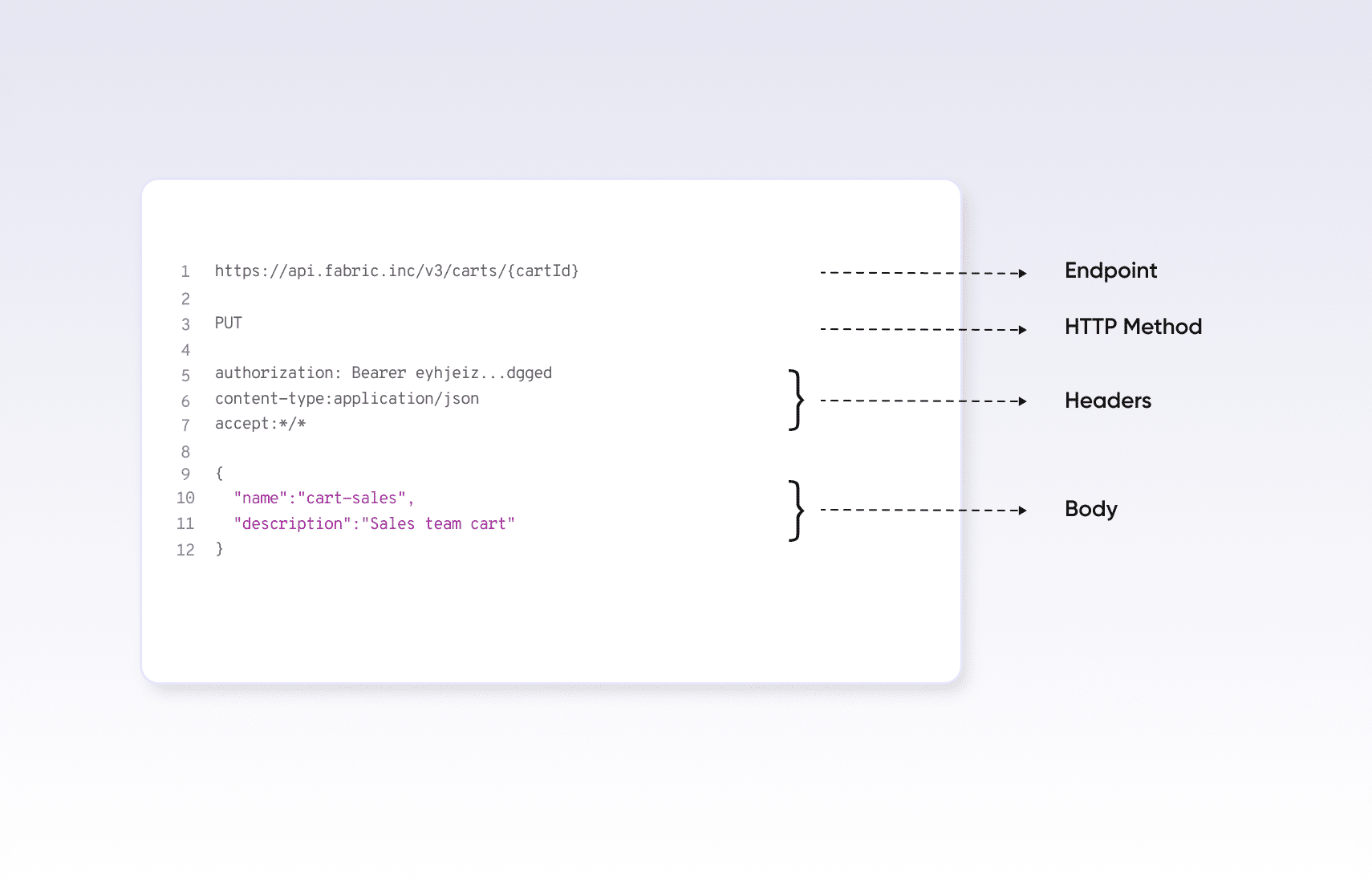
REST APIs use HTTP/HTTPS protocol for communication. A typical REST API request has 4 major components:
- 1. Endpoint – Endpoint is the URL which is a uniform resource identifier to locate resources on the web. It also optionally includes parameters depending on the request.
- 2. Http Method – Http method indicates what action needs to be taken with a resource.
- 3. Headers – Headers are used to pass additional information related to client and server. This includes content type, date/time, authentication details such as api key etc.
- 4. Body – Body is an optional component which is used to pass information to the server.
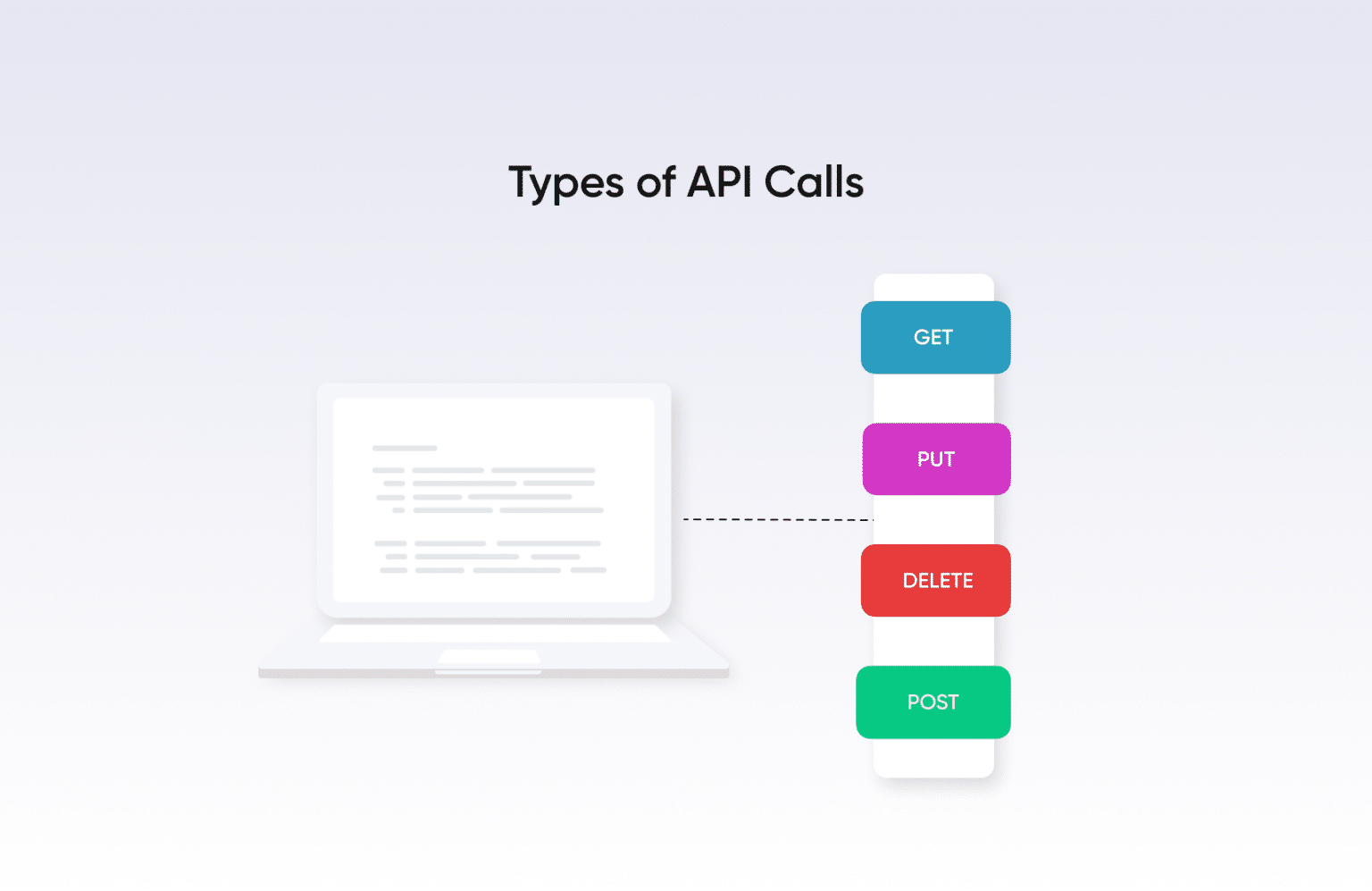
In an API call, the desired action is executed on a resource based on the HTTP method used. There are several http methods available which can be supported by the server, but the most commonly used are:
- GET – to retrieve a resource
- POST – to create a resource
- PUT – to update an existing resource
- PATCH – to update partial modification to an existing resource
- DELETE – to delete a resource
Below is an example of REST API request for adding an item to a shopping cart:
curl --location 'https://api.fabric.inc/v3/carts/b8a64b52-dab4-8137-8d6a-f2c2337abc1/line-items' \
--header 'x-fabric-tenant-id: 617329dfd5288b0011332311 \
--header 'x-fabric-channel-id: 12' \
--header 'x-fabric-request-id: 263e731c-45c8-11ed-b878-0242ac120002' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header 'Accept: application/json' \
--header 'Authorization: ' \
--data '{
"quantity": 1,
"itemId": 1730902008,
"sku": "16B2GS8LD5FDS",
"attributes": {
"productFamily": "Laptop computers"
},
"fulfillment": {
"type": "WEB_SHIP",
"networkCode": "ShipToHome",
"channelId": "12"
}
}'
Sample Response: 200 Success Response
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Date: Mon, 02 Oct 2023 17:48:23 GMT
Server: nginx
Content-Type: application/json
Content-Length: 66
{
"id":"123",
"sku":"16B2GS8LD5FDS",
"position":1,
"quantity":1,
"itemId": 1730902008
"createdAt:"",
"updatedAt":"",
"price":{
"currency":"USD",
"base":"100.0",
"sale":"80.0"
....
}
....
}
Sample Response: 404 Not Found Response
Date: Mon, 02 Oct 2023 17:48:34 GMT
Content-Type: application/json
Content-Length: 56
Connection: keep-alive
{
"code":"CART_NOT_FOUND",
"description":"Cart not found"
}
API security for safeguarding data transactions
With API calls, businesses must ensure there are robust security measures in place. Strong security can protect the integrity of data during exchanges between applications and systems. Implementing security measures prevents unauthorized access, data breaches, or malicious attacks that could compromise sensitive information.
Developers employ various techniques to enhance API security, such as using authentication mechanisms like API keys, tokens, or OAuth. Encryption plays a vital role in securing data in transit, guaranteeing that even if intercepted, the information remains unreadable to unauthorized entities.
Regular security audits, monitoring, and adherence to industry best practices further bolster the API Security framework. By prioritizing API security, developers not only protect sensitive data but also build trust and confidence in their applications.
fabric Identity (through Okta) provides a way to generate authentication tokens which is used to enable secure API calls. The system token generated using Client Credentials flow has expiration set to 10 mins by default. Once the token expires, it is expected to generate a fresh token to use for subsequent fabric API calls.
Refer this documentation fabric Identity authentication to learn more about how to generate and use a token to make secure API calls.
[toc-embed headline=”Step-By-Step Guide for How to Make API Calls”]
Step-By-Step Guide for How to Make API Calls
Here is a step-by-step guide for how to make API calls:
- 1. Identify the URI of the API to make a call. A typical URI contains a basepath or domain name, optionally followed by a resource that is being worked upon.
- 2. Once the endpoint is obtained, make sure to pass the correct HTTP method that is defined for the given API.
- 3. Next, all headers such as content-type, api key, or access token (if required by the API) needs to be provided in the request.
- 4. Depending on API definition, additional information can be provided to server application using optional request body.
- 5. Once the valid request is submitted, wait for a response from the API.
- 6. In the API response, you’ll receive a status code, optional response body, and various headers. The status code is crucial for discerning whether the submitted request was successful or encountered an error.
[toc-embed headline=”Designing Efficient API Calls “]
Designing Efficient API Calls
There are no certain guidelines on how one should design APIs, but there are a few important principles which need to be taken into consideration to maximize efficiency.
Documentation
Quality documentation is key to onboarding of developers to use APIs. That being said, it is very important that documentation is up to date with actual implementations.
- Guidelines and Examples: Well-defined documentation should have guidelines on how to use APIs. These should contain examples of requests and responses along with definitions of each element in both. This can be done through software tools like OpenAPI or postman. Including recipes on how to use APIs and providing sample curls can be very much useful as well.
Performance and Availability
As APIs provide a medium to exchange data over a network, performance and availability is of utmost importance. The following are some points that can be considered to maintain the performance and availability of APIs.
- Monitoring: Collecting a predefined set of metrics and monitoring the state of APIs can provide insights into API performance, usage patterns, and business relevance.
- Logging and metrics: Having structured logs and predefined metrics allow you to identify potential issues and monitor KPIs such as number of errors, latency, usage of APIs, etc…
Ease of Use
An aspect of how easily consumers can use APIs is an important part of API design.
- Proper requests and responses: APIs should have a well structured request and response body. An API endpoint should contain the name of the resource which will be accessed. For example, an API call to get the cart details, should use “/carts” in the request URL. Standard headers like content-type, authentication token, content-length, content-type should be used to share information. Using an appropriate HTTP method based on the request performed on a resource is crucial, as most developers are familiar with HTTP methods such as POST, PUT, GET, PATCH and DELETE and why they are used. For example, “GET /carts” indicate that this API call is to get cart details.
- Error Handling: It is very important for APIs to gracefully handle errors and return enough information with proper HTTP response codes. This allows consumers of APIs to understand any problems that occur.
- Pagination and Filtering Capability: Including pagination and filtering features in APIs is beneficial for tailoring API usage to consumer needs and improving response times.
- API Versioning: API versioning is essential to manage feature changes effectively, ensuring any updates or modifications do not disrupt existing implementations.
Benefits of using cache for APIs
APIs should be performant and responsive to provide the best shopping experience for customers. One way to improve API performance is by using a caching strategy. Caching means storing frequently used data temporarily for future use, enabling faster response times for subsequent requests.
Caching can be useful in the following scenarios:
- To manage heavy load: In case of heavy load on the API server, caching can be used to serve the processed data and reduce the load.
- To serve frequent requests: Data for repeated requests can be cached for subsequent requests and to improve overall response time.
Error handling in APIs
When designing efficient and well structured APIs, it is important to handle error scenarios gracefully. This can be achieved with consistent and well-defined error messages.
- Use of standard HTTP status codes: To indicate outcome of request. A few common codes include:
- 200 OK - Successful request.
- 400 Bad Request - Invalid request or could not be understood by the server.
- 401 Unauthorized - User is not authenticated.
- 404 Not Found - Requested resource not found.
- 500 Internal Server Error - An unexpected error occurred on the server.
- Use of error messages: Meaningful error messages give clear insights into problems that occur and help clients with troubleshooting.
- API documentation for errors: Clear documentation of all expected errors for the API can help developers to handle the errors effectively.
[toc-embed headline=”fabric’s Commerce Platform: Simplifying API Calls for Retailers”]
fabric’s Commerce Platform: Simplifying API Calls for Retailers
fabric Commerce Platform is a powerful, headless, API-first solution for retailers who are expanding their presence across multiple channels. It enables retailers to deliver superior shopper experiences through different APIs. Some of the benefits include:
- 1. Easy integrations – fabric’s API-first platform provides flexibility to work with existing stack or integrate with third party applications.
- 2. Developer flexibility – Developers can create and maintain highly customizable solutions using a suite of APIs provided to enable common shopper experiences like Add to Cart, Checkout, Inventory management.
- 3. Secure and faster APIs
Through fabric Commerce Platform’s different API calls, merchants can power up everything within e-commerce. The suite of API calls can help with managing inventory, setting up pricing and promotion strategies, managing cart and checkout, and creating and tracking customer orders—all the things needed throughout a shopper’s journey.
To learn more about fabric’s structured, secure, well documented suite of APIs, please visit fabric’s developer portal.
[toc-embed headline=”API Call FAQ”]
API Call FAQ
What is an API Call?
In simple terms, an API call is a medium to exchange data between two systems. It defines a set of rules to communicate between applications. Through an API call, the client makes a request to a server and gets a response back.
What is an example of an API call?
Let’s see how different APIs are used to manage a shopper’s cart during their shopping journey. As users add items to cart through online shopping sites, multiple API calls are made behind the scenes. One API call is made to the inventory service to see availability, another call is made to get the pricing details, and finally an item is added to cart.
Next time, when the user visits the website again, another API call is made to get the shopping cart with items added previously. The following is an example of rest endpoint to get the shopping cart details:
https://developer.fabric.inc/reference/getcartbyid
How do API calls work?
An API call can be viewed as a set of steps. First, a request is made to the server using an API endpoint along with request action, headers, and optional request body. The server receives this request and performs necessary actions using the backend program. Finally, data is provided in the response of the API call to the initiating client, along with the outcome of the request in terms of success or error codes.

Software Development Engineer @ fabric. Former Senior Java Developer @ MHK.